

About the programme
CGIAR, in partnership with the World Food Progamme (WFP) Innovation Accelerator, launched the Stability-and-Peace Accelerator to seek and scale high-impact innovations that bolster food, land, and water systems (FLWS) in fragile and conflict-affected settings (FCAs), where hunger and malnutrition is often felt most acutely.
The WFP Innovation Accelerator and CGIAR supported four ventures with groudbreaking solutions that can drive resilience, ensure food and nutrition security, enhance climate adaptability and promote social cohesion and sustainability among communities battered by conflict and fragility. Ventures received up to US$30,000 in equity-free grant support for implementing their sprint project and support and guidance from CGIAR and the WFP Innovation Accelerator to make their sprints successful. Alongside financial, technical and business support, the ventures also received scientific advising from CGIAR research centers aimed to improve the innovator’s ability to create life-changing sustainability impact.
These innovative solutions are not only innovative but also sustainable and scalable, with the potential to create lasting positive change in some of the world’s most challenging environments. They help end hunger, reinforce communities against unexpected disruptions, ensure consistent access to nutritious food, foster inclusive economic opportunities, engage youth and enhance the resilience of food systems amidst the challenges of climate change.
Selected innovations
Four ventures were selected to participate in a six-month sprint programme with CGIAR and the WFP Innovation Accelerator.

Aquaporo
AquaPoro is a state-of-the-art residential and commercial appliance that generates clean, drinkable water directly from the air by capturing, concentrating and condensing water vapour. The innovation offers a sustainable solution for households, schools and community centres. By collaborating with local partners, AquaPoro helps mitigate water shortages, improving access to safe water in resource-limited environments.
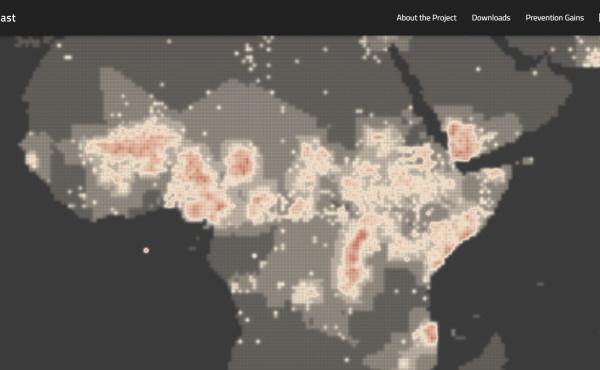
Conflict Forecast
Conflict Forecast is a platform that integrates granular maps of conflict forecasts, agricultural collapse and population to highlight potential displacement hotspots.

iPlant
iPlant addresses the challenge of sustainable food production in urban areas by offering an innovative, scalable solution to vertical farming that reduces space, energy costs and reliance on artificial lighting. In collaboration with private and public partners in Jordan, iPlant supports local food production, helping mitigate water scarcity, support growing urban populations and adapt to climate change. The innovation offers a cost-effective and efficient way to produce fresh food in urban environments.

Koolboks
Koolboks freezers are transforming businesses by keeping food fresh longer, cutting electricity costs and boosting profits. Many customers have reduced their energy bills, with some abandoning the national grid entirely. Business owners gain an average of five extra selling hours daily, increasing income, while those selling perishables see spoilage losses drop by 70 percent. This simple yet powerful solution is improving livelihoods in off-grid communities.
Priority areas
For this Innovation Challenge, CGIAR and the WFP Innovation Accelerator sought both low and high-tech solutions specifically tailored to meet the distinct challenges present in Fragile and Conflict-Affected Settings (FCAs) specifically in Jordan, Kenya, Nigeria and Yemen. We also encouraged strong “wildcard” entries. We aimed to identify and support exceptional innovations from around the world that hold the potential to address these challenges on a significant scale. WFP’s and CGIAR’s current innovation priorities per country are listed below:
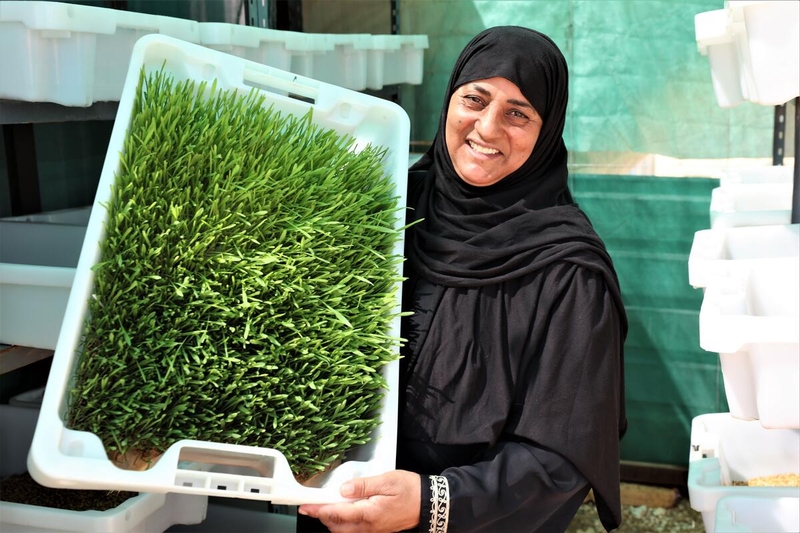

Jordan
Water and resilience in refugee and host communities
Examples may include water purification systems for refugee and remote communities, irrigation systems, soil health monitoring technology, urban agriculture, or vertical farming that enhance water access and resilience.
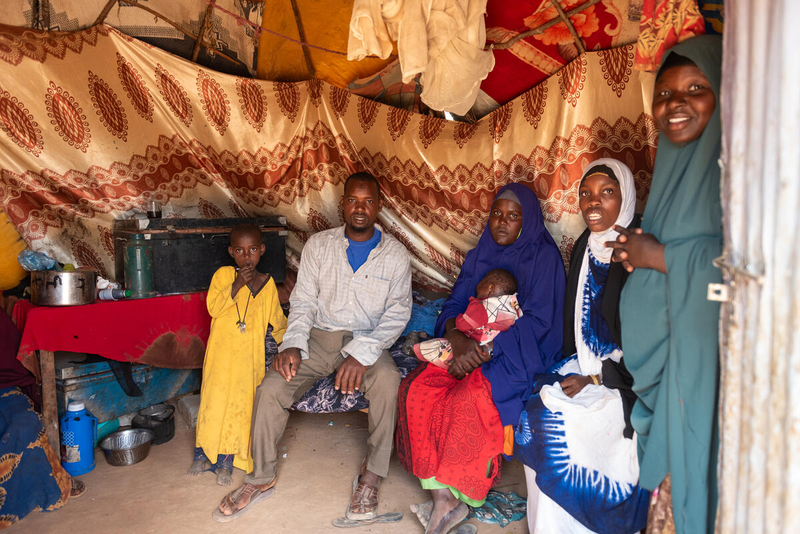

Kenya
Digital solutions for climate security and migration
Examples may include forecasting for environmental disasters, conflict prediction and mitigation technology, communication resources for refugees or mapping technology to identify displacement patterns.
Nigeria
Resilient food systems and nutrition
Examples may include cold-storge solutions to prevent post-harvest loss, food fortification, mobile platforms for smallholder farmers, agricultural technology for resource management or technologies that increase shelf life.




